1. Structure of the Water Molecule
a. molecular formula:
structural formula:
b. Why is water bent?
2. Polarity of the Water Molecule
a. compare electronegativities of O and H
i. O has two partial _______ charges
ii. H has a partial _______ charge
b. more info
i. Why is oxygen negative?
ii. How much water is in living things?
1. Hydrogen bonding of water
2. Cohesion of water
a. H-bonds form between which atoms in
water?
b. Water can form up to ___________
H-bonds.
c. The attraction between water molecules
is called ______________, and it results from hydrogen bonding.
d. Why can water form four hydrogen
bonds?
3. Dynamics of Hydrogen bonding
1. Organizing Effects of Water
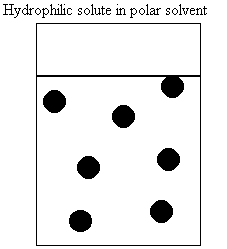
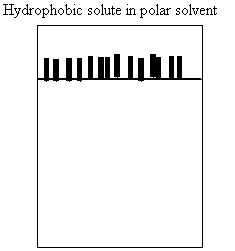
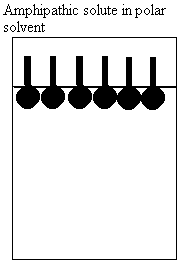
a. How do molecules behave in water?
i. nonpolar
ii. polar
iii. amphipathic
b. Why don't oil and water mix?
c. Do molecules break apart when they
dissolve?
d. Does water repel nonpolar molecules?
e. Does water treat all polar molecules
alike?
2. Chemical Reaction with Water
3. Tensile Strength of Water
a. tensile strength:
b. cohesion
c. adhesion
d. Why do paper towels sop up water?
4. Surface Tension of Water
a. surface tension is a result of:
b. Why don't all small objects float on water?
c. demo: overfilling a dish
d. Other molecules disrupt the surface
tension of the water.
i. What happens to the water in the dish
when the surface tension is disrupted?
ii. What was used to disrupt the surface
tension of the water?
iii. How do detergents make water wetter?
5. High Specific Heat of Water
a. water can gain or lose heat with
little change in temperature because:
b. How does water's specific heat affect
organisms?
c. What is kinetic energy?
d. Why do hydrogen bonds cause high
specific heat?
6. Cooling by Evaporation
7. Boiling
a. What happens to H-bonds during
boiling?
b. The bubbles in boiling water are.....
c. The temperature stays the same in
boiling water because:
8. Why Ice Floats
a. How does the density of ice compare to
the density of liquid water?
b. arrangement of molecules in ice:
c. arrangement of molecules in water:
d. How does the density of ice affect
life?
9. Freezing
a. What happens to the water molecules as
they freeze?
b. What is a lattice?
c. Can ice evaporate?