A. What is Organic?
1. Original definition:
2. Chemists definition:
3. Yet another definition:
B. Why is carbon special??
1.
2. Chemistry
a.
b.
c.
d.
C. General Structure
1. carbon skeleton
2. functional groups
D. Carbon Skeletons
1. C bonds 4 other atoms
2. branched, straight chain structures
3. more info
a. Why is C so important to life?
b. Why does C bind 4 other atoms?
c. Do other atoms ever interrupt a carbon skeleton?
E. Functional Groups
1. intro
a.
b. What is the difference between a male and a female?
2. Hydroxyl group (aka alcohol)
a. structure:
b. ionize?
c. polar?
d. forms H-bonds?
e. Where can I find hydroxyl groups?
3. Carbonyl Group
a. structure:
b. ionize?
c. polar?
d. forms H-bonds?
e. Where can I find carbonyl groups?
f. What are aldehydes and ketones?
4. Carboxyl Group
a. structure:
b. ionize?
c. polar?
d. forms H-bonds?
e. Where can I find carboxyl groups?
5. Amino Group
a. structure:
b. ionize?
c. polar?
d. forms H-bonds?
e. Where can I find amino groups?
6. Sulfhydryl Group
a. structure:
b. ionize?
c. polar?
d. forms H-bonds?
e. Where can I find sulfhydryl groups?
7. Phosphate Group
a. structure:
b. ionize?
c. polar?
d. forms H-bonds?
e. Where can I find phosphate groups?
8. Recognizing Functional groups within molecules
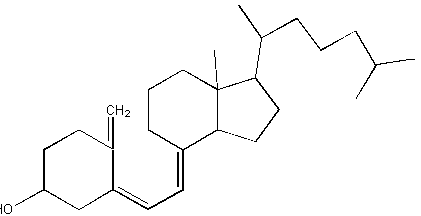
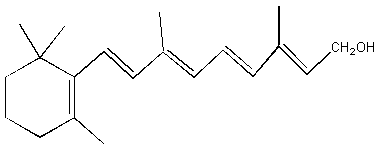
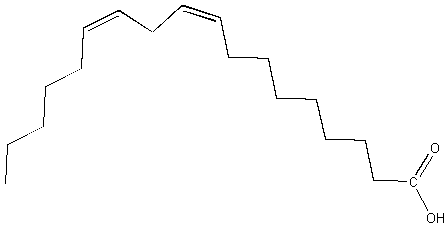
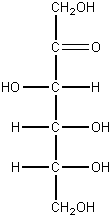
a. vitamin B2
b. vitamin D
c. vitamin A
d. linoleic acid
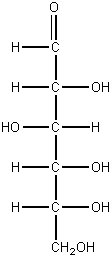
e. glucose f. fructose
F. Isomers
1. Structural
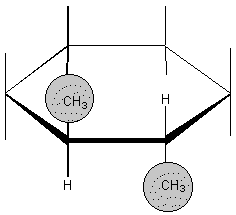
2. Geometrical
a. definition:
b. Examples:
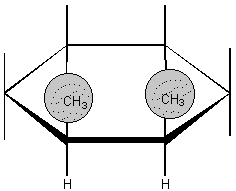
c. In what types of molecules do they occur?
i.
ii.
d. Why do they occur?
e. Naming geometrical isomers
i. cis-
ii. trans-
3. Enantiomers
4. more info
a. Why should I care about isomers?
b. What is I eat the wrong isomer?
G. Polymers
1. Intro
a. monomers
b. polymerization
2. Examples of polymers
a. polysaccharides
monomer is ______________
b. proteins
monomers are _______________
c. teflon
monomer is _________________
d. deoxynucleic acids
monomers are ________________